Post-industrial Waterfront Planning and Design with Multi-perspectives
----A case study of Bailian Jing River District planning implementation project, Shanghai Expo
LIU Yue-Qin LIN Xuan-Quan
《Journal of Landscape Architecture in Asia》 Oct-2008

Abstract:
Among the diverse characteristics of waterfront regeneration of post-industrial era, recreational function is one of the most important of them. In the case of Bailian Jing River district planning implementation program, Shanghai Expo, the urban waterfront plan and design under the dual challenges of “post-industrial era” and “great urban event” was discussed. The problems encountered in updating the industrial remains waterfront, for example, the relationship between flood control and recreation, historical context extension, heatstroke prevention in summer, high-density evacuation of visitors flow, the usage problems between during and after Expo, the coordination between pump, watergate, bridge and environmental problems, should be solved in a comprehensive manner. The purpose is to regenerate the public waterfront to harmonize with the urban environments.
Key words:
Post-industrial Landscape;Shanghai Expo;Bailian Jing River District (BJRD);Waterfront Landscape;Problems and Solutions
1 Introduction
1 Preface Introduction
Due to the transformation of economic development mode and the transportation means in the post- industrial era, a large number of waterfronts which used to be preoccupied by industrial bases and terminal ports have been under gradual decline. Since the 1960s, the Western developpeddeveloped countries began to step into the post-industrial era which was characterized by knowledge economy ; leisure activities then came to play an remarkable role in the structure of people's daily life. Both the renewal and reconstruction of the waterfronts and Continuouscontinued efforts in the development of the leisure falloweconomy initiated from North America since the beginning of the era had close ties with this historicalthe environmental context[1] at that time.
The banks Both shores of Huangpu River in Shanghai are the birthplace of China’s the Chinese modern industry and also the initial and emerging area of the Chinese national industryChina’s national industry. A host of industrial architectures witnessed the development of Shanghai as Modern China’s emerging industrial city. The 2010 Shanghai World Expo, as the comprehensive Expo with the theme of city, will be the first comprehensive Expo to be held in developing countriesy firstly. The site of the Expo is located in the downtown urban area between the Nanpu Bridge and the Lupu Bridge across the Huangpu River. This grant event of Shanghai can serve as a booster for further development of the city and will also pose a profound impact on the leap-forward development of urban space. The banks shores of the Huangpu river calls for a transit of functions from the industrial economy to consumer economy in order to attractpush people back to the waterfront area, meanwhile to extend the historical and cherished context of this area. Moreover, the objective here is to transform this area into a comprehensive waterfront greenbelt integrating different functions such as sight-seeing, leisure, tourism and education, thereby promotinging the development of Shanghai water tourism and achieving achieving the rejuvenation regeneration of the city’s urban waterfront area. (Figure 1)
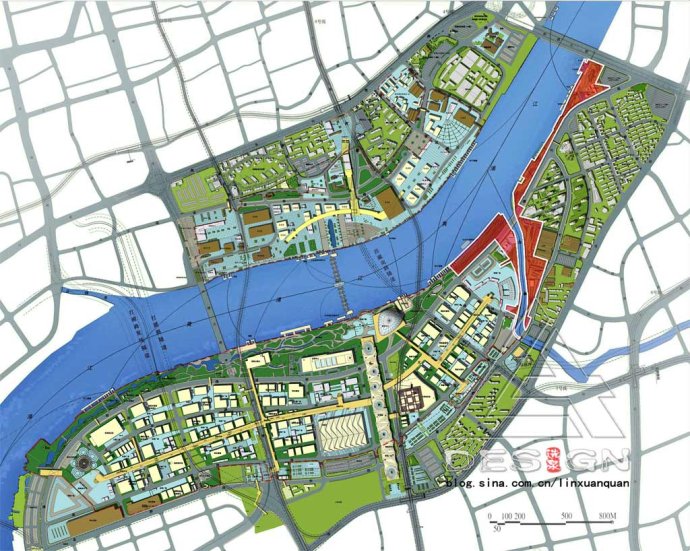
Fig.1: Master plan of Shanghai World Expo in 2010 and the planning scope of BJRD
2 Multi-perspective objectives of Bailian Jing River District
The structure of the green space system of Shanghai Expo area consists of “one core, one axis, two belts and multiple wedges”. The waterfront greenbelt is composed of Bailian Jing riverside greenbelt, the World Expo Park and the back Bund Park. With the Huangpu River in the north, the mere Bailian Jing River inside the Expo Park in the south, the Expo Village in the east and the Expo Park in the west, the Bailian Jing River District (short for BJRD in the latter content) covers an area of 23 hectares (Figure 2) and is filled with quantities of factories, warehouses, wharves, docks and other facilities, which are typical productions of the industrial age.

Fig.2: Bird-view landscape from different angles of the planning implementation projects of BJRD
In view of the post-industrial context and special characteristics of the Expo site, the planning of the BJRD should focus on its geographical characteristics and be oriented to ecology, science, technology and culture, the three of which should be taken into consideration in a harmonious way. The specific function of the BJRD and its further application after the Expo should be considered in a coordinated way. Moreover, the implementation of the BJRD should be carried out in harmony with the surrounding facilities such as bridge, pump-gate and revetment to create a dynamic and diverse comprehensive public waterfront space (Figure 3).
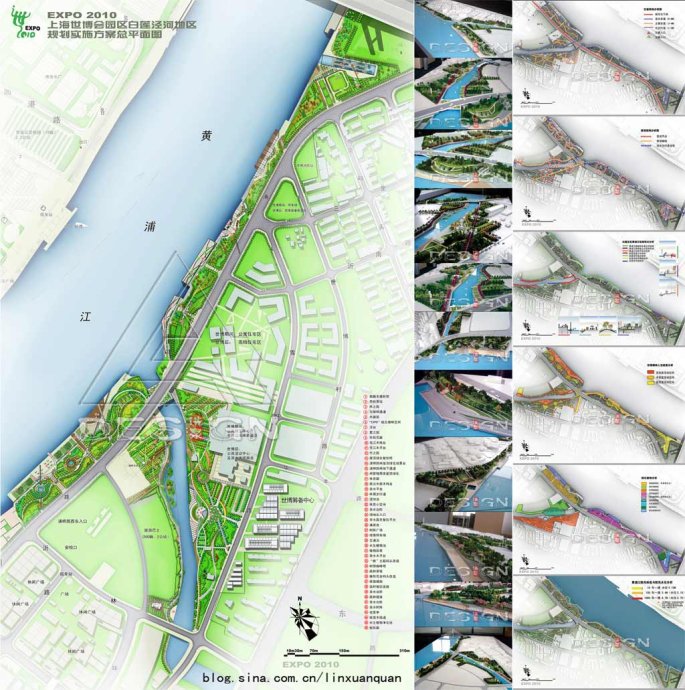 Fig.3: Master plan of BJRD and analysis charts Fig.3: Master plan of BJRD and analysis charts
3 Site problems and landscape solutions
From the trend of "fear of water" in the industrial era of to the trend of "close to water" in post-industrial era, from docks and terminals in the past to the dynamic waterfront public space nowadays, all of which have shown the relationship between human and nature is harmonious and unified, rather than confrontation and conflicts. On the basis of rising the landscape concern of post-industrial era on ecological environment, the re-utilization of industrial wastes and diversification of leisure patterns[2], the planning of BJRD should focus on solving several major site problems and achieving the transformation of several concepts, namely, the relationship between flood control and water-enjoyable recreation, historical context extension, heatstroke- prevention and temperature-cooling in summer, high-density visiting flows of evacuation and assembling ,the usage problems between during and after Expo, the coordination between pump, water-gate ,bridge and environment and so on.
3.1 Problems and solutions on flood- control and water- enjoyable recreation
In the industrial age, high embankments (mostly in hard vertical way) are built for flood control and the city safeguard. This kind of protection is not only costly but also can bring unsatisfactory results since it may break the natural balance between the water and the greenery, which could not solve the problem completely. Since 1990s, views on the regulation of river tended to change all over the world. Firstly, countries like Switzerland, Germany and Japan put forward the concept of “natural bank revetment” to replace the traditional view of “paving bank revetment”. Secondly, changes took place in the concept of flood control from adopting measures of “bend cut-off” in the past to today’s measures of “plugging combined with dredging, flood discharging along with sluicing” [3].
Since Bailian Jing waterfront green space in post-industrial era should deal with flood control and water recreation, the "Greenery Wave" concept are proposed from three different perspectives. Firstly, the macro-perspective of the "City Green Wave" is under the urban open space and structure of green space. Secondly, the mid-perspective of the "Huangpu River Green Wave" is under waterfront public space. Lastly, the micro-perspective of the "Expo Green Wave" is under the functional structure of the Expo park. The concept "wave" implies the ongoing power and the transfer of function like waves after waves. Through the creative idea of “wave”, the gap between today's Huangpu River and the whole Shanghai city is expected to be no longer insurmountable..
In the specific design, the method of reusing old flood prevention wall and setting natural ecological revetment to construct a diversified water space of different levels will be used to appeal people back to the waterfront to enjoy the change of tide and appreciate the enhancing beauty of the nature.
There are two rivers flowing in BJRD, one is the Huangpu River designated with the millennium - flood control criterions, and the other is would-be inner river---Bailian Jing River. In light of the different river types, they should be dealt with in different measures.
3.1.1 Bank revetment space design in Huangpu River
As the mother river of Shanghai, the Huangpu River is a medium intensity tidal river with two ebbs and flows every day. The average high tide for the river is +3.14 meter, with the average low tide +1.29 meter. Ground elevation along the river is about +4.20 meter, with the highest water level in 10 years up to +4.73m, in 100 years up to +5.18 meter in 1000 years up to +5.70 meter, and the height of floor prevention wall is designed to be +6.70meter.
Neither the one-layer flood-prevention walls in Puxi Bund nor the two-layer terrace flood embankment in Lu Jiazui can fundamentally solve the water-enjoyable problem.. So people can only feel the width of the Huangpu River, but can not enjoy the change of tide. Nevertheless, the water-enjoyable problem of the Huangpu River is not only a visual aesthetics, but also a technical one.
The greatest difficulty for the water-enjoyable problem lies on the vertical L-ferroconcrete flood prevention walls which stand along the Huangpu River with a height of +2.5meter and a total length of 1.7 km. Most of the walls were built in the 1990s with a huge investment..
The first problem to be solved here is whether the flood-prevention wall can be reused to cut down the cost and embody the principal of “thrift-advocating world exposition”. Through structural stability examination and calculation, the existing flood-prevention wall could totally satisfy the requirements, which indicates that the
wall and the fundamental structure can be remained and the part of the original wall with the height over +4.7 meter can be removed (Figure 4).
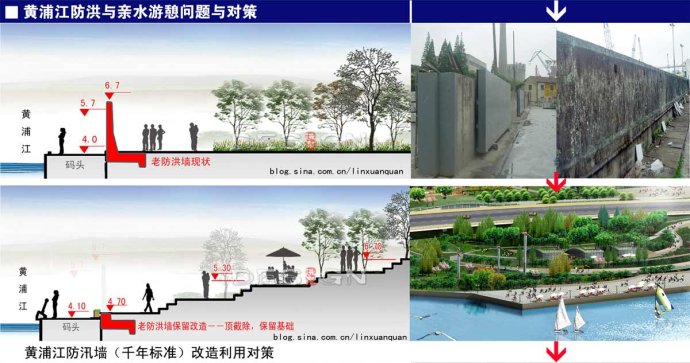 Fig. 4: Measures for transformation and utilization of the existing flood-prevention wall in Huangpu River Fig. 4: Measures for transformation and utilization of the existing flood-prevention wall in Huangpu River
Then, one paradox arises, after the removal of the upper level of the wall, how can the flood happening with the possibility of once in a thousand year be prevented? The plan here adopts the means of “little stall wall combined with flood prevention wall”, that is, the part between+ 4.7meter and +5.3 meter can be replaced with hard little stall wall, while the part above +5.3meter can be the soil-made flood-prevention embankment . The material of dike itself is silty-clay, the slope of which is laid with vegetation. As first-class water-enjoyable facilities, the key point here is how the silty-clay embankment could satisfy the requirements of flood control. Through calculation on “antiskid, antiroll, anti-deformation “,
the embankment can well satisfy the requirements, which lays a firm foundation for creating diverse waterfront space.
Since the feasibility of water-enjoyable engineering makes it possible to replace the vertical flood control wall with a flood embankment, then the next step is how to integrate the flood embankment and the diversified waterfront landscape space. In the specific design the creative idea of "Green Wave" will be promoted, which means layers of flood embankment with the shape of slope are combined with waterfront open space with different levels to satisfy people’s different demands for water-enjoyable space. Specific measures are as follows (Figure 5):
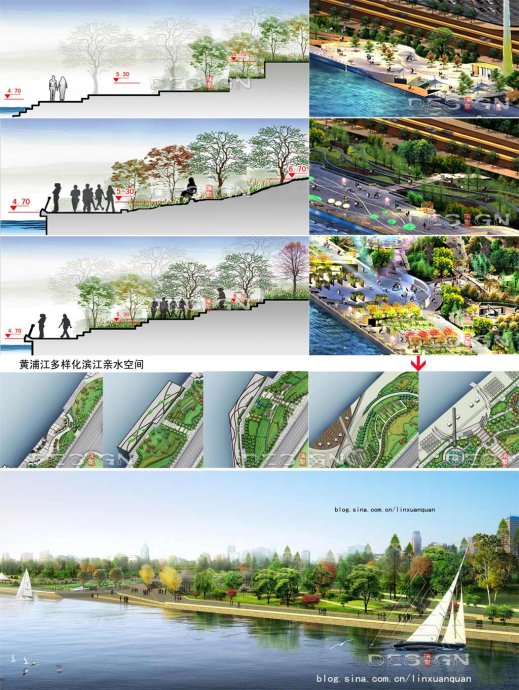 Fig5: Measures for flood-control and water -enjoyable recreational space in Huangpu River Fig5: Measures for flood-control and water -enjoyable recreational space in Huangpu River
(1)step-into-water style: set layers of steps gradually into water in partial section to form a completely water-enjoyable space with a height of+ 2.20~3.00 meter.
(2)slope-step water-enjoyable style: set some temporary leisure facilities and architectures to form a sub water-enjoyable space while reserving a large number of terminals at the elevation of +4.0 meter in the venue.
(3)waterfront walkway: set the +4.00 meter wide waterfront walkway at the elevation of +4.70 meter in the highest navigable water level and make it interpenetrate the entire waterfront area.
(4)main leisure space: set waterfront overlook space and leisure space at different elevations in the space above+5.30 meter. Some permanent leisure facilities and architectures at the waterfront can also be set at this elevation.
3.1.2 Waterfront revetment space design in Bailian Jing Inner River
According to the requirements of water resources planning, since the navigation function of Bailian Jing
River is to be abolished and a new pump-gate will be build at the estuary to bear the drainage task, the Bailian Jing River will become the only inner river in the Expo Park zone. The water level of the Bailian Jing River is similar to inner rivers, usually between+2.50 meter and +2.80 meter, the highest control water level is +3.75 meter and the ground elevation is controlled within+4.20 meter, therefore, the above-ground part of the Bailian

Fig. 6: Measures for transformation and utilization of the existing flood-prevention wall in BJRD
Jing flood control wall for the millennium can be removed (Figure 6). After turning the Bailian Jing River into an inner river, planners list several landscape strategies to diversify the waterfront space and to create an ecological and natural waterfront revetment. Specific measures are as follows (Figure 7):
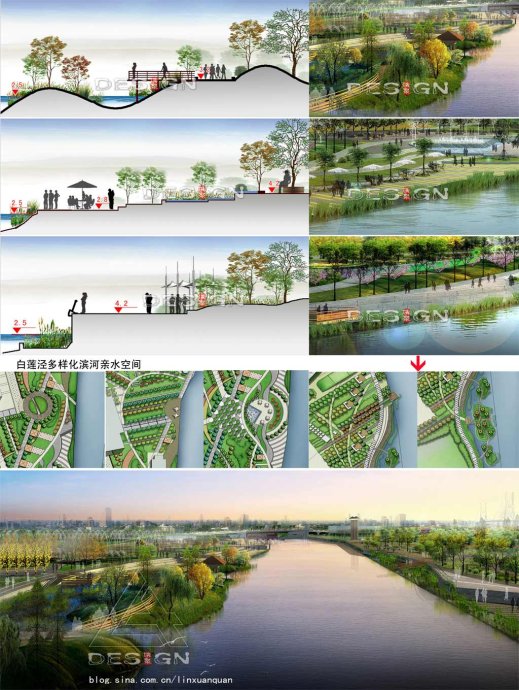 Fig.7 Measures for flood-control and water-enjoyable recreational space in Huangpu River Fig.7 Measures for flood-control and water-enjoyable recreational space in Huangpu River
(1)Propose creative concept of “green wave ”. Digging some wetland isles in local districts can not only expand the size of wetted cross section and the capacity of adjusting storage which is beneficial to flood prevention and river flow rate decreases, but also enrich the shape of river water body, and enhance the diversity of the river landscape.
(2)Construct a multilevel flood embankment or build a wooden trestle to realize multiple water-enjoyableness .
(3)Set several shoreline elevations equal with the road surface and some water-enjoyable outrigger platforms to reduce digging and save costs.
(4)Apply bio-engineering methods to some revetment despite hard revetment. Bio-engineering technology adopts naturally-degradable materials to protect the bank slope before the formation of revetment vegetation.. It has many advantages such as low maintenance requirements, fast habitat restoration, low cost, nature-contact and has been applied currently in Shanghai (such as ecological river of Pudong Airport town). The revetment of those wetland isles can take the form of ecological riverbank protection, which is to implant hygrophyte (trees,brushes and grasses), emerged plant, floating-leaved plant and submerged plant sequentially from the top to the toe of the slope. This kind of protection can be applied in the concave site of the river and the gentle slope with less current scour. At the banks of the digging wetland isles, the shrub layer intercalation protection can be applied, that is planting living branches with or without roots horizontally in a cross or repeated way (cuttage) in the soil layer of the slope. It’s suitable for the river reach with steep slope and large surface runoff[4].
3.2 Continuous waterfront public pedestrian system
In order to make the urban waterfront more dynamic, pedestrian traffic should be encouraged. Thereby a well-pedestrian system with strong accessibility and water-enjoyableness is to be promoted here.
Currently the total annual number of tourists visiting the Huangpu River is less than 1% of that of tourists visiting Shanghai. An important reason for this phenomenon is that the shoreline along the river is occupied by large numbers of industrial facilities and few public shoreline places are available for visitors to access freely. In view of this, the design of the Expo riverside green space should reflect the future development trend. In addition to giving the industrial shoreline back to people to embody organic mix of publicity and multi-functions, the planning should also take the waterfront space into consideration to build a feasible waterfront pedestrian road. The pedestrian road will link various key landscape nodes along the Huangpu River and Bailian Jing River, connecting the Expo Park in the south and Huangpu riverside green land in the north, thereby a smooth, diverse, hydrophilic and enjoyable waterfront pedestrian system can be formed.
3.3 Diverse waterfront experience space
A dynamic waterfront area needs organic blend of various functions. Several experience units with the theme of fog, forests and bamboo respectively can be built along the riverside belt with 4.7 m above the highest navigable water level. That is, to build a fog park, a forest park and a bamboo park which function as nodes to satisfy visitors’ demands for leisure and recreation (Figure 8).
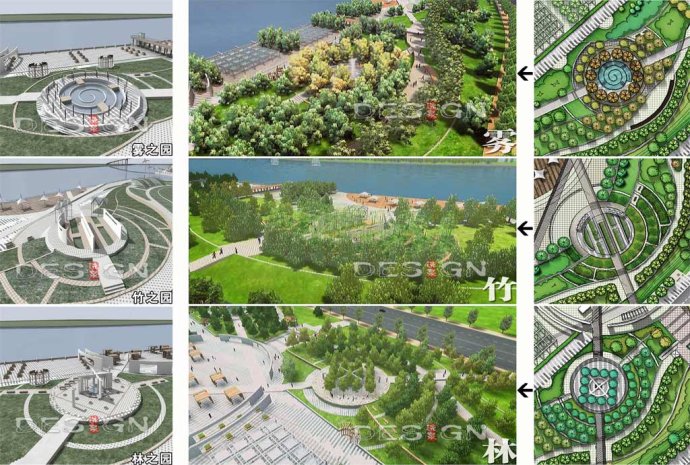 Fig. 8 Multi-experience units in the waterfront area: Fog Park, Bamboo Park and Tree Park Fig. 8 Multi-experience units in the waterfront area: Fog Park, Bamboo Park and Tree Park
Besides, many other experience units of different functions can be set along the riverside, replacing industrial terminals with a multi-functional hydrophilic square, turning the dock into a drop biological purification display area, renewing the tower crane into a viewing platform and arranging some riverside tearooms or coffee bars which are hiding in the slope of the green.
Since several drowning incidents have happened in some rivers such as Zhang Jiabang river, the safety facilities along the Huangpu riverside must be taken into serious consideration. The whole space of riverside should be separated without resistance while the forms of these safety facilities can be diversified. Despite a set of protective railings which are characteristic of the waterfront area, shelters can be used to keep the security of visitors. Protective measures can also be carried out combined with some facilities such like suppository ship rivet and also, arranging some life buoys or other life-saving facilities at a safe distance repeatedly can be helpful too.
3.4 Problems and strategies on historic context extension
One feature of old industrial waterfront area in a city is that it often witnesses a certain historical period of the urban development and retains abundant traces of the urban history. The waterfront landscape affiliated to this specific condition also bears some characteristics of this era, then embodying some unique features and characteristics of the site..In view of the complexity of the inheritance and development of the historic context of the site, initiative and creative actions should be carried out.
Through analysis and summarization, four ways are raised to deal with the historical context extension of the industrial remains:
(1)Industry elements reservation(Figure 9)
Due to the characteristics of the original industrial base, some structures which are of industrial characteristics can be found in the Expo site such as the chimney of the industrial age, some industrial components in the substation. This kind of structures can be retained and processed into industrial sculpture.
 Fig. 9: First strategy for site context extension : industrial parts reservation Fig. 9: First strategy for site context extension : industrial parts reservation
(2)Function transformation(Figure 10)
The large hydrophilic piers in the site, after checking its structural safety, can be turned into multi-functional waterfront leisure square, or a cultural square of industrial site features with its own characteristics. For example, arrange some removable shade scaffolds in the piers and set up some public service facilities for viewing, rest, refreshment, rental, inquiry, etc.
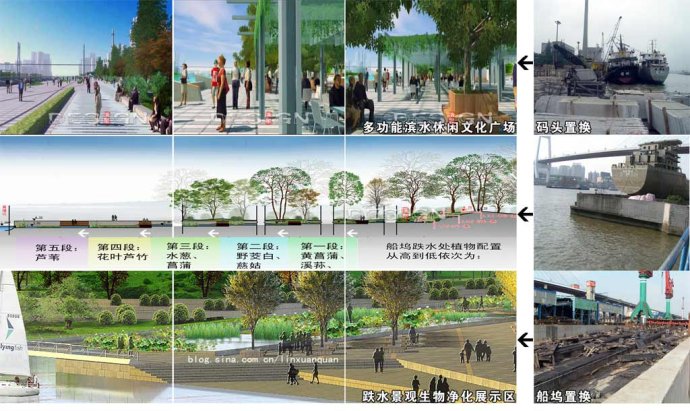 Fig. 10: Second strategy for site context extension: function transformation Fig. 10: Second strategy for site context extension: function transformation
The Shanghai Edwards shipyard dock which lies in the northeast corner can be turned into a "drop landscape biological purification display” area through function replacement. The dock has a length of 170 meter and a height difference of 2.2 meter which can be used to design a drop landscape zone of five different layers. The lowest layer will be connected with the Huangpu River and each layer will be covered with soil to plant some water sewages which can adapt to the corresponding water level and have strong ability to tolerant and absorb pollution. Through water flows and the role of aquatic plants, the water can be oxygen-aerated and purified.
Plants at each layer will be: yellow flag and iris sanguinea, Zizania aquatica L and arrowhead, black rush and acorus calamus, giant reed and reed. The whole drop landscape here transits from elaboration to wild pleasure. The wooden plank road will run through the entire water-enjoyable drop landscape area and emerge into the Huangpu River. Visitors can walk through the entire area, viewing the Huangpu River in a close distance and enjoying the tidal change of the Huangpu River.
F
(3)Transformation and re-utilization (Figure 11)
Through inspection and analysis, structures in the Expo venue which are in line with the requirements of supporting services and facilities can retain its structure and be modified in the faade and the interior space. After the Expo, these structures can be kept for other usage or removed according to the architectural usage and the subsequent development.
 Fig. 11: Third strategy for site context extension: transformation and renewal Fig. 11: Third strategy for site context extension: transformation and renewal
(4)Re-utilization of the deserted wastes (Figure 12)

Fig. 12: Fourth strategy for site context extension: reutilization of waste
Many traces of the industry and daily life are left in the site, such as small gray bricks, building bricks, tiles, industrial components, etc. These can be reused and be processed into distinct landscape facilities operculum.
3.5 Problems on Heatstroke-prevention and temperature- cooling in summer
Hot days with high temperature account for nearly two thirds of the exposition period from May to October in the year 2010. The challenge here is how to create a cool and comfortable visiting environment for high-density tourists. The main measures are as follows:
1) Temperature-cooling of green land and water: large square multi-layers greenery is constructed to display the cooling role by the green land.
2) Temperature-cooling of roof greenery:mature roof green technology is applied to all kinds of public service facilities and water-enjoyable constructions.
3) Aerial green networks: vertical greenery is combined with avenues、tree-matrix plazas 、flower-corridor pergolas and so on to build aerial green networks.
4) Fog spray technology:TTC fog spray technology is adopted to change “water” into “fog” to achieve the multiple results of temperature decrease, scenery making, humidity control and dust diminishing.
3.6 Problems on high-density visiting flows assembling and evacuating
As predicted, in the 184-day-long period of Shanghai Expo, there will be over 70-million tourists from all corners of the world to get to the site, with a average-day flows up to 400 thousand, general-day flows up to 600 thousand and peak-day flows to 800 thousand. As one of main eight exits of the exposition park, the Bailian Jing Square will have 14-thousand visitor flows in the peak hour during the Expo according to traffic prediction. The waterfront belt which is connected with the square then can also serve as a pressure-reducer to evacuate flows and relieve the pressure that high-capacity visitors posing on the core district of the park .The detailed strategies are as follows:
1) Set terminal traffic points and straight-line road networks: in order to benefit the flows to evacuate, accesses are placed in the traffic terminal points in the Puming Road; in addition, the straight-line roads are designed to help people reach waterfront district more quickly and conveniently.
2) Reuse original docks and add more hard pave tiles: most of berths and docks are reserved, and more paving area are added in the area, the capacity of which has been calculated scientifically to satisfy the requirement of people’s staying and relaxing.
3) Rooster tree-matrix squares: a tree-matrix square with more tree shade is built in the crucial node points to respond to sudden flush of flows.
4) Plan open forest grassland: the way of “tree and turf” is adopt in the place which will hold accounts of people to provide a short-stop place with shelter and lower temperature. After the end of the exposition, flower shrubs and slopes will be added under these tresses, creating multi-layer plants landscape and improving spatial green view rate.
3.7 Usage problems between during and after Expo
Surveying from several earlier waterfront world expositions, the waterfront area can always been improved a lot for drawing support from the expo, and changed into a dynamic urban waterfront park, becoming an excellent recreation place for citizens. Based on that principal, the green space in Bailian Jing is planned to be perpetual land, which will be reserved after the expo. Except for the temporary green land on the east side of the BJRD, original function of BJRD can be kept. Moreover, market operation system can be brought into this area, for example, small-size dining facilities can be set there, aiming to construct an open waterfront leisure commercial district with lasting and dynastic multi-functions.
4. Problems on the coordination between pump, water-gate, bridge and environment
In waterfront areas, on account of irrigation works, grand hydraulic structures should be built,, such as pump-gate bridges, and then there arises the challenge of dealing with the relationship between hydraulic structures and environment which requests a perfect combination between “hydraulic technology and landscape art”. According to the plan, in the mouth of the Bailian Jing River, one check gate and one second-class pumping station should be built; moreover, from the perspective of the integration of the landscape and engineering,, the “pump and floodgate integration” approach is adopted to spare the occupied land. In order to solve the problem of over-large volume of pump - gate facilities, the pump-gate are placed one-side, and the check gate are hid as
lying door ; the exterior surface of the pump station can be ornamented with circular abstract pattern, which diminish dull and bulky of the concrete; the top of the pump and floodgate mixed with green plants can be accessible to visitors and used as sightseeing platform; detection bridge of the pump-gate can be designed as a pedestrian bridge connecting the two sides of the Bailian Jing River. What to be addressed here is that through the integration of technology and art, the pump -gate can be harmonious with neighboring environment to the maximum extent, and also serves as one scenic spot amongst all the waterfront landscapes.
According to the plan, a Puming Road Bridge should be built in the site of the pump and gate. Then, two different projects are proposed, one is “pump divided with bridge” and the other is ‘pump connected within the bridge “(figure 13). Through comprehensive analysis of the projects and landscapes, the latter plan is chosen in which the pump gate will be 70 meters away from the bridge. Main merits of the plan are the effects imposed on the hydrophilic of two-side space of river will be reduce to the least by the flood-prevention wall outside the pump and floodgate without ruining picturesque scenery of the Puming Bridge ; the pump is separated from the bridge and constructed stage by stage .

Fig. 13: Different ways dealing with relationship between pump gate and bridge: “separated and integrated”
The approach of “bridge landscape CI theory “[5]is applied in the design of the Puming vehicular bridge and the Bailian Jing pedestrian bridge(figure 14). Under the guide of the unity of engineering and landscape, the bridge type is chosen and the unique feature is defined. Seen from the whole world exposition and waterfront contour line, the Puming Bridge located at the river mouth do not need any landmark; what it needs is “the harmony with the environment, so the three-span continuous frame arch bridge is the final choice which can deal

Fig .14: Landscape of the Puming vehicular bridge and Bailian Jing pedestrian bridge
well with the contradiction between the bridge and the flood-prevention wall. The main body of the bridge and its affiliate facilities are designed systematically. The color and night view of the bridge are designed specifically, which can strengthen visitors’ perception of the Puming Bridge.
5. Other pending problems and strategies
In addition, plants, night view lighting and landscape architectures in BJRD waterfront belt should be designed separately, for example the 3R principle should be applied in public service architecture design to weaken architecture form and allow green to penetrate into the inner space of architecture, turning the architecture into a inseparable element growing from the environment, reaching the perfect combination of the two. What worth to be mentioned here is that the design should not be trapped in the absolutization of technological and ecological aesthetics. Instead, the principal landscape designer should uphold is that to create waterfront landscape architecture with characteristics of times and geography, also taking society and culture factors into consideration.
-------------------------------------------
Appendix:
Bidding Award: the First Prize in bidding of the international competition in 2006
Award:
the third prize of the Sixth Works Competition of (international) Youth Architects in Shanghai in 2007
Acknowledgment to the partner –the technological support from the Shanghai Investigation, Design & Research Institute on the pump gate design
References:
[1] Liu Yueqin, Lin Xuanquan. Planning and Design of Urban Waterfront Recreation Landscape for Zhangjiabang, Shanghai Pudong [J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture,2006(2):25~30
[2] Zhangjing, Dingqi. A Study on Post-industrial Landscape [J]. Journal of Nan Jing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition) ,2007(2):96~100
[3] Liu Xiaotao. Discussion on Problems of City River Harnessing [J]. Water Resources Planning and Design , 2001(3):28~33
[4] Li Xiaopin, Zhang liquan. Application and effectiveness of soil bioengineering in ecological restoration of stream bank [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2006(9):1705~1710
[5] Lin Xuanquan, zhang Dawei. CI Theory and Practice of Bridge Landscape [J]. Urban Roads Bridges & Flood Control, 2005(2):11~15
-------------------------------------------
Author:
Liu Yue-Qin:
Born in 1978, Female, Ningde in Fujian province/ PhD candidate in College of Architecture and Urban Planning in Tongji University/Research field: landscape planning and design (shanghai 200122 liuyueqin999@163.com)
Lin Xuan-Quan:
Born in 1978, Male, Datian in Fujian Province/ Master candidatel graduate in the College of Architecture in TianJin University/ Director of the landscape planning and design studio of Pudong Architecture Design and Research Institute, Limited Company /Research fields: landscape planning and design (shanghai 201204 linxuanquan@163.com)

|
 信息产业部网站备案:沪ICP备13040278号-1
信息产业部网站备案:沪ICP备13040278号-1
 沪公网安备 31011502003788号
沪公网安备 31011502003788号

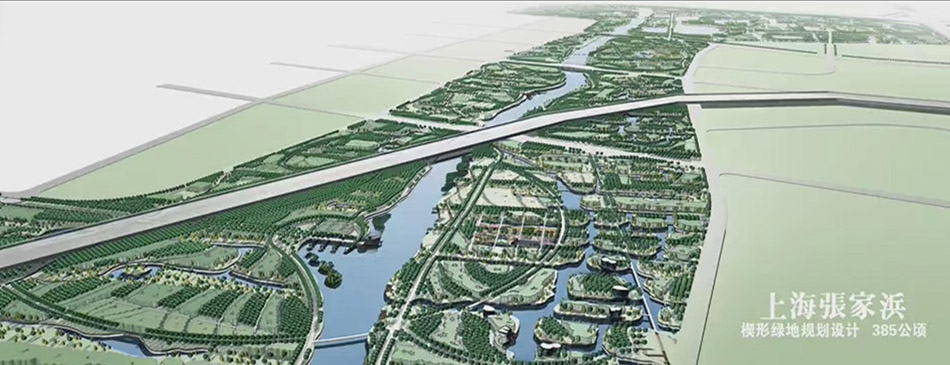









 Fig.3: Master plan of BJRD and analysis charts
Fig.3: Master plan of BJRD and analysis charts
 Fig. 4: Measures for transformation and utilization of the existing flood-prevention wall in Huangpu River
Fig. 4: Measures for transformation and utilization of the existing flood-prevention wall in Huangpu River
 Fig5: Measures for flood-control and water -enjoyable recreational space in Huangpu River
Fig5: Measures for flood-control and water -enjoyable recreational space in Huangpu River

 Fig.7 Measures for flood-control and water-enjoyable recreational space in Huangpu River
Fig.7 Measures for flood-control and water-enjoyable recreational space in Huangpu River
 Fig. 8 Multi-experience units in the waterfront area: Fog Park, Bamboo Park and Tree Park
Fig. 8 Multi-experience units in the waterfront area: Fog Park, Bamboo Park and Tree Park
 Fig. 9: First strategy for site context extension : industrial parts reservation
Fig. 9: First strategy for site context extension : industrial parts reservation
 Fig. 10: Second strategy for site context extension: function transformation
Fig. 10: Second strategy for site context extension: function transformation
 Fig. 11: Third strategy for site context extension: transformation and renewal
Fig. 11: Third strategy for site context extension: transformation and renewal



